STEP 1 Review the imaginary strand of DNA below. I will go ahead and explain the entire process of DNA replication.

Dna Replication S Phase Checkpoint Control Learn Science At Scitable
This means that each new molecule of DNA contains one strand of the parent molecule and one complementary strand that is newly synthesized daughter strand.
. STEP 3 Draw the free-floating RNA bases linking up. Draw the free-floating RNA bases linking up with the top side of the DNA strand. You will use the STEP 1 Review the imaginary strand of DNA below.
The two strands of DNA have to be temporarily separated from each other. The first step of PCR heats the sample of double-stranded DNA dsDNA to melt it and separate the strands. This step uses heat.
Bases are added smoothly in the 5 to 3 direction. Step 3 Draw the free-floating RNA bases linking up with the top side of the DNA strand. Step 4 Draw the new mRNA strand and the rezipped DNA strand.
STEP1 Draw the original DNA strand from Exercise 7 below. A complementary strand is created for each of the two strands of the original double helix. The information in RNA although copied into another chemical form is still written in essentially the same language as it is in DNAthe.
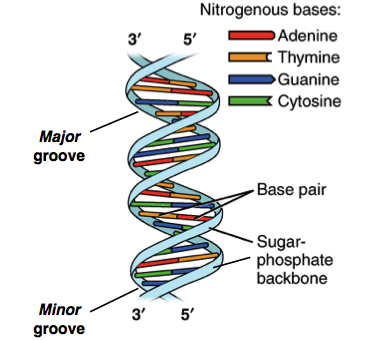
This job is done by a special enzyme helicase that helps unwind and separate the DNA helices Figure 6. Draw the dna strand separating down the middle Written By leary Friday April 8 2022 Add Comment Edit. DNA replication is semi-conservative.
The DNA double helix breaks or unzips down the middle between the base pairs. Note the complementary base pairs. People need to pump install a pump to push the water to the surface from confined aquifiers.
Now that you understand the basics of DNA replication we can add a bit of complexity. There short pieces of DNA called Okazaki fragments are made by DNA polymerase with the help of a short RNA primer and then joined together by another enzyme called DNA ligase. STEP 3 Draw the free-floating RNA bases linking up with the top side of.
Draw the DNA double helix with the sequence on the 5 to 3 strand. A G C A A T C C G T C T T G G T C G T T A G G C A G A A C C Step 2. Remember in protein synthesis only one side of the DNA strand is used Be sure to follow the rules of complementary base pairing and to account for the special RNA base uracil.
AGCAATCCGTCTTGG TCGTTAGGCAGAACC STEP 2 Draw the DNA strand separating down the middle as in the beginning of DNA replication. STEP 3 Draw the free-floating RNA bases linking up with the top side of the DNA strand. The enzyme DNA polymerase moves along the exposed strands and adds complementary nucleotides to each nucleotide in each existing strand.
Extensive studies for more than twenty years have established that type II topoisomerases use a two gate mechanism for DNA strand passage 3 10 11 in which a DNA duplex the transport or T-segment is transported through an enzyme-mediated transient opening in a separate DNA duplex the gate or G-segment. Step 2 Draw the DNA strand separating down the middle as in the beginning of DNA replication. Draw the DNA strand separating down the middle as in the beginning of DNA replication.
Original strands of DNA one for the leading strand and one for the lagging strand. A G C A A T C C G T C T T G G T C G T T A G G C A G A A C C Step 3. Draw write the free-floating RNA bases linking up with the top side of the DNA strand.
One strand is called the leading strand. Note the complementary base pairs. The other strand is called the lagging strand.
Draw write the DNA strand separating down the middle as in the beginning of DNA replication. Draw the DNA strand separating down the middle is in the beginning of DNA replication. Draw the DNA strand separating down the middle is in the beginning of DNA replication.
STEP 2 Draw the DNA strand separating down the middle las in the beginning of DNA replication. Use your notes and any other resource necessary for help. Newer Post Older Post Home.
STEP 1 Review the imaginary strand of DNA below. Note the complementary base pairs. Portions of DNA Sequence Are Transcribed into RNA.
Draw the DNA strand separating down the middle as in the beginning of DNA replication. Note the complementary base pairs. Another issue is that the DNA polymerase only works in one direction along the strand 5 to 3 but the double.
The 5 and 3 ends of DNA pronounced five. The first step a cell takes in reading out a needed part of its genetic instructions is to copy a particular portion of its DNA nucleotide sequencea geneinto an RNA nucleotide sequence. Remember in protein synthesis only one side of the DNA.
You must label all the bold words in each drawing and indicate the 5 and 3 ends of each strand with direction arrows. Hence two newly generated molecules remain similar to the parent DNA molecule. 0 Response to draw the dna strand separating down the middle Post a Comment.
This job is done by a special enzyme helicase that helps unwind and separate. STEP 1 Review the imaginary strand of DNA below. Remember to follow the rules of complementary base pairing and to account for the special RNA base uracil.
Note the complementary base pairs. AGCAATCCGTCTTGG TCGTTAGGCAGAACC STEP 2 Draw the DNA strand separating down the middle as in the beginning of DNA replication STEP 3 Draw the free-floating RNA bases linking up with the top side of the DNA strand Remember in protein synthesis only one side of the. PCR works to amplify a small sample of DNA.
AGCAATCCGTCTTGG TCGTTAGGCAGAACC STEP 2 Draw the DNA strand separating down the middle as in the beginning of DNA replication.

Dna Replication Steps Diagram Expii
When Dna Is Replicated Or Copied The Ladder Splits As The Bases Separate New Units Are Added To Each Half Of The Dna Molecule How Does This Create Two Identical Molecules Of

Dna Replication S Phase Checkpoint Control Learn Science At Scitable

Dna Replication Leading Strand Vs Lagging Strand Okazaki Fragments Youtube

Dna Structure And Replication Review Article Khan Academy
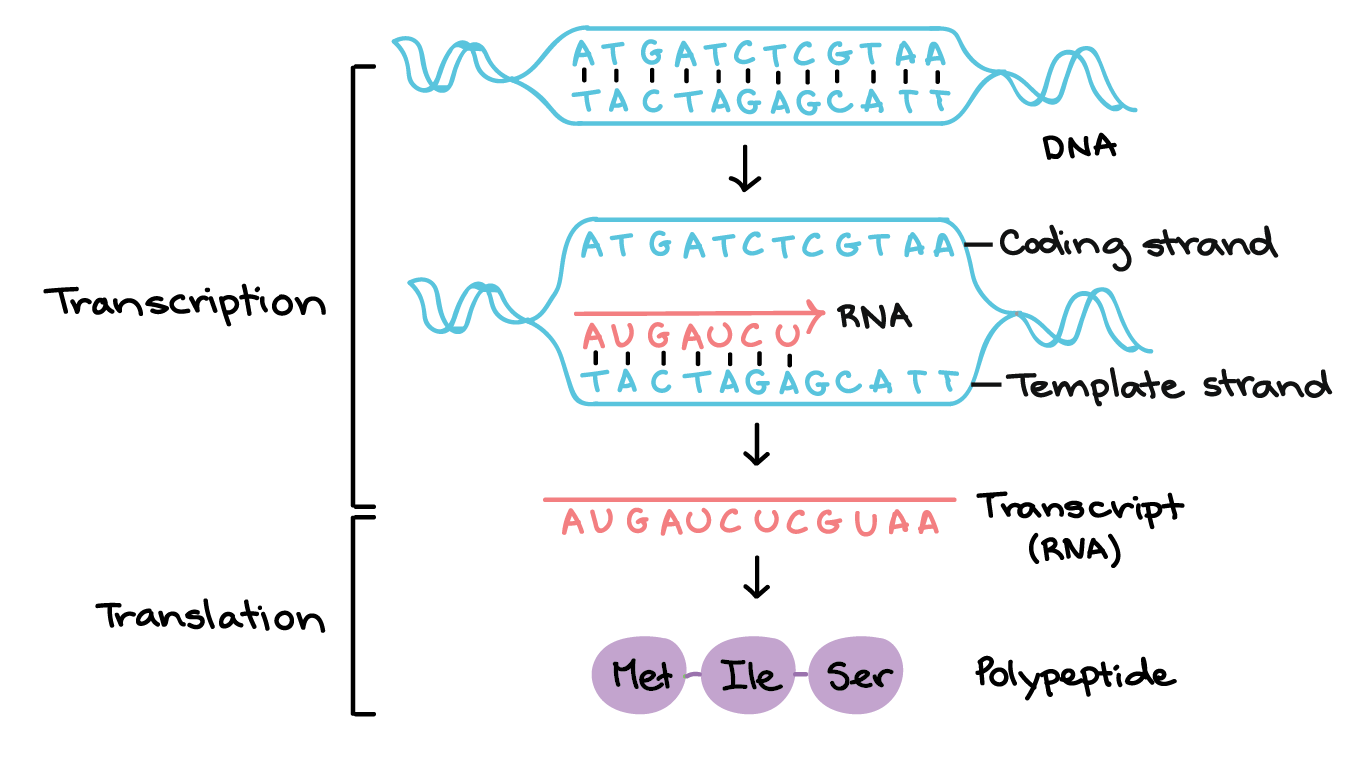
Stages Of Transcription Initiation Elongation Termination Article Khan Academy
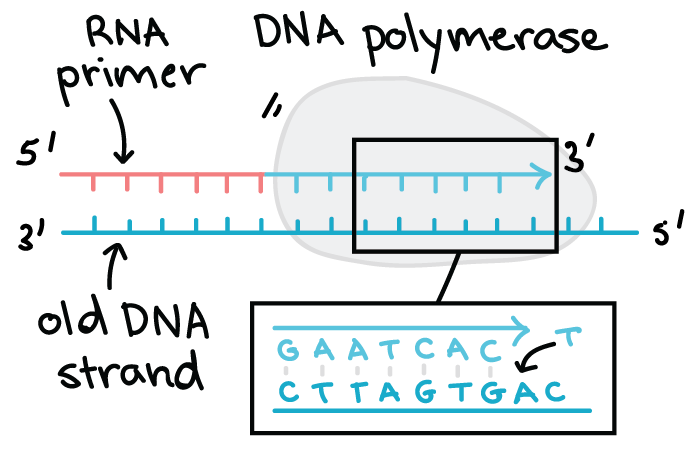
0 comments
Post a Comment